Welcome to Practicalkida, in this blog post, we share the Strength of Materials SOM 313308 IMP for the MSBTE Winter 2024 examination.

Strength of Materials 313308 subject is common for mechanical and civil engineering students.
SOM 313308 IMP For Winter 2024 Exam
Unit – I Moment of Inertia
- Define i) Moment of Inertia and ii) Radius of Gyration. State its S.I. unit
- State Parallel Axis Theorem.
- State Perpendicular Axis Theorem.
- Define the polar Moment of inertia
- A hollow circular section with 200 mm external and 100 mm internal diameter. Using the parallel axis theorem calculate M.J. about any tangents.
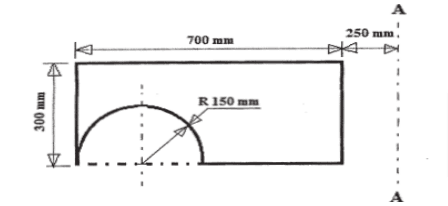
- Calculate the moment of inertia about the axis A-A, for the lamina shown in the Figure.
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a hollow rectangle about an axis passing through a base 200 mm in size.
- The internal and external dimensions of the rectangle are 160 mm × 260 mm and 200 mm × 300 mm, respectively.
- An asymmetrical I-section of an overall depth of 300 mm has flanges 150 mm × 10 mm and a web 10 mm thick. Calculate the moment of inertia @ XX and YY censorial axes.
- Find the moment of inertia of angle ISA: 100 mm × 75 mm × 6 mm about the centroidal XX and YY axis.
- Calculate the M.I. of a T-section about the centroidal xx axis. Top flange is 1200 mm × 200 mm and the web is 1800 mm × 200 mm. The total height is 2000 mm.
PDF:
Unit – II Simple Stresses, Strains & Elastic Constants
- Define shear strain and modulus of rigidity.
- State the relation between Young’s modulus and Bulk modulus.
- Draw a stress-strain curve for ductile material showing salient points on it. Also, define yield stress and ultimate stress on it.
- Define Poisson’s ratio and state the relation between three elastic constants E, G, and K.
- Define Creep and toughness.
- Define stress and strain and state its S.I. unit.
- E = K. Calculate E/G & Poisson’s ratio for a certain material.
- In a tri-axial stress system, the stresses along the three directions are σx = 100 N/mm2 (tensile), σy = 60 N/mm2 (tensile), and σz = 30 N/mm2 (compressive). Find the strains in each direction. Take E = 2 × 105 N/mm2 and μ = 0.25. If X = 400 mm, Y = 150 mm, and Z = 300 mm. Also calculate the volume change.
- Neat sketches show the failure of the rivet in single-shear and double-shear. Also, write the formulae to calculate shear stress for each case. Assume the diameter of the rivet = d.
- A steel tube of 40mm inside diameter and 4 mm metal thickness is filled with concrete. Determine the stress in each material due to an axial thrust of 60 KN. Take E for steel = 2.1 x 105 MPa. E for concrete = 0.14 x 105 N/mm2
- A metal bar 200 mm long, 40 mm × 30 mm in cross-section is subjected to stress of 110 MPa along the length and 50 MPa on the other two faces. All stresses are tensile. Calculate strains along the three directions and also the volumetric strain. Assume E = 120 MPa and μ = 0.30.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we share the Strength of Materials SOM 313308 IMP for the MSBTE Winter 2024 examination. If you think this blog post is helpful then share it with your friends.



Please give a important question with solution
Sir please important questions with solutions and thank you for send important questions
Important questions with solutions highway engineering/ advanced surveying/ concrete technology/ strength of materials please sir with solutions dedo
Important question