Welcome to PracticalKida, in this post we solved TEN 313310 Manual Practical No.2. In this practical we Measured of discharge of air using an air box.

Many industries require precise measurement and control of airflow rates for efficient operation
of equipment and processes. Students will have to perform tests of reciprocating air compressors,
and IC engines, and measurement of convective heat transfer coefficient. In all these cases calculation of the airflow rate at the inlet of these devices is important. Students shall be able to
calculate this flow rate which is expressed in m3/s.
TEN 313310 Manual Practical No.2 Required Resources
| Sr.No | Name of Resource | Suggested Broad Specification | Quantity |
| 1 | Reciprocating air compressor test rig | Pressure gauge ranges from 0 to 10 bar, Water Manometer U-shaped glass tube, Orifice plate diameter 6 to 30 mm, Air box, speed up to 650 rpm. | 01 |
- Fill the manometer with water up to half level.
- Keep the delivery valve and manometer cock on the suction line in closed position.
- Start the compressor and open the manometer cock. Then, let the air pressure build-up in
the tank. - Run it till tank pressure becomes 2 bar.
- Maintain the pressure of air inside the tank constant, by adjusting the delivery valve.
- Open the air delivery valve so that tank pressure will not rise further.
- Take manometer reading.
- Measure the intake air temperature (T1) at the suction of the LP cylinder.
- Calculate air flow rate in m3/s.
- Repeat the same procedure by increasing pressure by 2 bar in each step.
Observations and calculations
Observation Table:
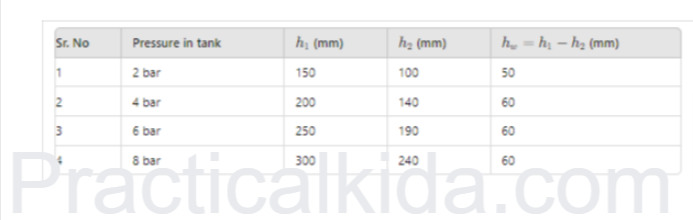
Calculation:
- Density of air

- Water manometric head

- The air ahead causes the flow of air

Practical Related Questions
- Which types of instruments are typically used in an air box setup to measure air discharge
accurately?
Answer:

- List the factors that affect the accuracy of air discharge measurements using an air box.
Answer:

- Write an equation of state and state meaning of all terms involved with their units.
Answer:
PV = nRT
- Pressure (P): The force exerted by the gas per unit area.
- Volume (V): The space occupied by the gas.
- Amount of Substance (n): The quantity of gas, measured in moles.
- Ideal Gas Constant (R): A physical constant relating the energy scale in physics to the temperature scale. Its value is approximately 8.314 J/mol·K.
- Temperature (T): The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules, measured in Kelvin.
- If the pressure of the atmosphere changes what will be an effect on the volume
flow rate of air at the inlet of the compressor?
Answer: The volume flow rate of air at the inlet of a compressor is directly proportional to the atmospheric pressure.
Conclusions
We successfully completed TEN 313310 Manual Practical No.2 in which we Measured of discharge of air using an air box.


